The efficiency and longevity of any industrial electronic system—from server racks and inverters to complex automation machinery—rely fundamentally on effective thermal management. Component failure, system throttling, and unexpected downtime are often the direct results of a poor cooling strategy. When designing or upgrading a system, the fundamental choice between Alternating Current fans and Direct Current DC fans is critical, impacting everything from the system’s power efficiency and reliability to its ultimate cost of operation.
Here, we wil provides a definitive, expert comparison based on core technical differences, application suitability, and total cost of ownership (TCO). By the end, you will understand the nuances to select the optimal fan technology for your industrial needs.
AC Fan vs DC Fan
| Feature | AC Fan Summary | DC Fan Summary |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower (Higher TCO) | Higher (Lower running cost) |
| Speed Control | Fixed (Limited control) | Excellent (PWM, Voltage control) |
| Longevity | Rugged but limited control | Highly reliable (LINKWELL 50,000+ Hrs) |
| Noise/EMI | Generally higher | Generally lower (Ideal for sensitive systems) |
| Wiring | Simple (Direct line power) | Requires DC power supply |
Power Consumption & Efficiency
When converting electrical power into mechanical airflow, DC fans are inherently superior.
- DC Fans: They utilize high-efficiency Brushless DC (BLDC) motors, minimizing energy lost as heat. This results in far lower running costs and reduced heat generation within the equipment itself, which lessens the overall thermal load.
- AC Fans: These fans use induction, which creates more resistive heat. For the same airflow output, AC fans will generally consume more power than their DC counterparts, leading to higher Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) over the fan’s lifetime.
Speed Control & Intelligence
Control flexibility is a major deciding factor for modern, intelligent systems.
- DC Fans: Highly flexible and “intelligent.” Their integrated PCB allows for precise speed control using external signals like Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) or voltage regulation. This enables closed-loop cooling, where the fan speed adjusts dynamically based on component temperature—critical for high-density hardware.
- AC Fans: Limited flexibility. Speed is fixed by the power line frequency. While variable frequency drives (VFDs) can be used, this adds significant cost and complexity, and is rarely practical for smaller fan applications.
Longevity & Reliability
Reliability is measured not just by component quality but by operational design.
- DC Fans: While their electronics can be sensitive to voltage spikes, modern industrial DC fans built by manufacturers like LINKWELL are designed for extreme durability. Our high-quality BLDC fans are rated for an exceptional MTBF (Mean Time Between Failure) exceeding 50,000 continuous hours, often utilizing robust ball bearings.
- AC Fans: Their mechanical simplicity makes them physically rugged, but the internal friction and lack of soft-start capabilities can sometimes lead to reduced lifespan compared to optimized DC fans, particularly in applications with frequent start/stop cycles.
Noise Profile & EMI
DC Fans: Generally quieter. The precise electronic commutation minimizes vibration and magnetic noise, making them the preferred choice for noise-sensitive environments and high-density computing. They also produce lower Electromagnetic Interference (EMI).
AC Fans: Can be noisier due to motor hum and less precise mechanical rotation, and their reliance on high-voltage AC power can result in higher EMI.
Voltage and Installation
AC Fans: Simple installation; they connect directly to standard line power (e.g., 110V/220V). No power conversion is necessary.
DC Fans: Require a low-voltage DC power supply (12V, 24V, 48V). In systems connected to AC mains, a dedicated power supply or converter is needed, which adds a component cost.
Application of AC Fan
AC fans are widely used across industrial environments where consistent airflow, high operating durability, and stable power supply are required. Designed for continuous duty, they perform reliably in harsh conditions such as high-temperature, dusty, or vibration-heavy environments.

Industrial Control & Power Systems
AC fans are extensively used in control cabinets, power distribution units, and automation systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures for sensitive components such as PLCs, relays, inverters, and power modules. In enclosed electrical environments, heat buildup can lead to performance degradation, system faults, or equipment shutdown.
AC fans ensure steady airflow and effective heat dissipation, supporting continuous production processes in factories, workshops, and industrial clusters. They help improve equipment lifespan, reduce failure rates, and maintain stable operation under demanding conditions.
HVAC, Ventilation & Environmental Equipment
Heating, ventilation, and air-handling equipment rely on AC fans for high-efficiency airflow delivery and long-term durability. From air filtration units and dust-collection systems to industrial dehumidifiers and cooling units, AC fans help regulate airflow and maintain indoor environmental stability.
Their simple integration and high durability make them ideal for 24/7 continuous-duty equipment. These applications benefit from AC fans’ excellent endurance in dusty, humid, or temperature-fluctuating environments, ensuring consistent performance in mission-critical air control systems.
Heavy Machinery & Manufacturing Lines
Industrial machinery such as CNC equipment, metal processing machines, plastic injection molding lines, compressors, and welding systems generate significant heat during operation. AC fans provide direct airflow cooling to motors, bearing housings, electrical enclosures, and drive assemblies.
Their rugged construction and strong airflow output support reliable heat dissipation in high-vibration, high-temperature working environments. This ensures smooth operation, prevents overheating shutdowns, and enhances manufacturing efficiency, especially in continuous-production facilities.
Application of DC Fan

Power Electronics & Renewable Energy Systems
DC fans are core components in energy storage cabinets, photovoltaic power conversion systems, EV charging stations, and advanced power modules. These applications demand efficient cooling in confined spaces while maintaining stable airflow under fluctuating load conditions.
With features such as PWM control, tachometer feedback, and alarm output, DC fans actively adjust cooling based on system temperature and workload. This ensures optimal thermal balance, enhances semiconductor longevity, and improves operational efficiency in next-generation energy systems.
Server, Networking & Telecom Infrastructure
In data centers, 5G base stations, and telecom cabinets, thermal stability is essential to avoid latency, system dropouts, or component failure. DC fans excel in high-density electronics environments due to their low noise output, variable-speed control, and compact structural design.
These fans maintain steady airflow with minimal vibration and provide precise cooling for CPUs, power modules, optical modules, and network routers, proving critical to modern high-bandwidth and ultra-connectivity networks.
Industrial Automation & Precision Equipment
Robotics platforms, AGVs, CNC drives, sensors, and motion-control systems rely on DC fans for accurate, energy-efficient heat management.
Their fast response, adjustable performance curve, and long bearing life support reliable cooling even in dynamic duty cycles and confined industrial housings. DC fans provide superior cooling adaptability, making them essential in advanced industrial automation environments where precision, compact structure, and long-term stability are fundamental.
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
When selecting a cooling solution for industrial applications, evaluating upfront price alone is not enough. The true value lies in the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes energy consumption, system efficiency, maintenance, service life, and downtime risk over the product lifecycle. Both AC and DC fans provide reliable cooling, but they deliver different long-term economic performance depending on the application environment and operational demands.
Energy Consumption & Operating Costs
DC fans typically offer higher energy efficiency due to brushless motor technology and smart speed control. In applications requiring dynamic cooling or continuous operation, DC fans can reduce power consumption by up to 70% compared to fixed-speed AC fans.
AC fans remain cost-effective for applications with stable cooling demand, but DC fans generally provide lower long-term operating expenses in variable-load environments.
Maintenance & Service Life
DC fans generally feature longer lifespan bearings and produce lower heat inside the motor, resulting in extended operational life and reduced maintenance cycles.
AC fans are highly durable in fixed-speed environments but may require more frequent replacement in precision-controlled systems.
System Efficiency & Downtime
Intelligent functions such as PWM speed control, tach feedback, and alarm signal outputs give DC fans an edge in predictive maintenance and system efficiency. These features help prevent overheating, reduce downtime, and support proactive system monitoring — key factors in mission-critical industrial operations.
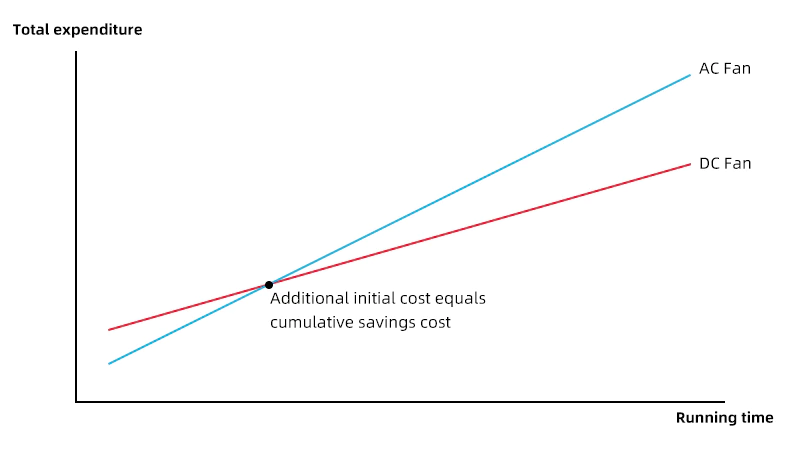
Investment Summary
AC Fans: lower upfront cost, excellent for stable industrial cooling, long-term reliability in standard applications.
DC Fans: higher initial investment, lower long-term energy and maintenance costs, ideal for precision, high-density, and smart control environments.
Choosing the right fan type improves reliability, lowers lifecycle cost, and maximizes system performance.
For industrial applications that are of high intensity (such as 24/7 operation), have high electricity costs, and have extremely high requirements for reliability (with high downtime costs), the “break-even point” of choosing DC fans will be reached very quickly, making it an obvious and wise investment.
Conclusion
Selecting between AC and DC fans depends on your system requirements, energy priorities, and performance expectations.
AC fans offer strong durability, stable operation, and cost-effective cooling for traditional industrial environments. They are ideal for constant-load systems where simplicity and reliability matter most.
DC fans, powered by advanced brushless motor technology, deliver precise speed control, higher efficiency, and longer operating life — making them the preferred choice for smart electronics, energy-storage systems, high-density servers, and automation equipment.
While DC fans carry a higher initial investment, they significantly reduce long-term operating and maintenance costs, supporting improved performance and lower total cost of ownership.
Whether your priority is stability and cost efficiency or intelligent control and energy savings, choosing the right cooling solution ensures system reliability, extended equipment lifespan, and optimized thermal performance.
Your cooling system is not just a component — it’s a core investment in your equipment’s performance, safety, and future scalability.
Ready to Upgrade Your Cooling System?
Let our engineering team help you evaluate the best fan solution for your application — AC or DC.

